Health Inequity
Philosophy
The unequal geographic distribution of healthcare resources in sub-Saharan Africa is a major impediment to the achievement of UNAIDS’ goal of eliminating inequities in accessing antiretroviral therapy – a cornerstone of its recently announced strategy for ending the HIV pandemic. Our current research focuses on designing new methods to measure inequities and finding new solutions to reduce inequities.
Current Research Project
Health geographics, HIV epidemiology and medical deserts
We are measuring geographic inequities between communities in access to antiretroviral therapy, and exploring different strategies to minimize these inequities. We are doing this by using a novel geospatial modeling framework that we have developed. This framework can be applied in any sub-Saharan African country; we are currently applying it to Malawi. We are working with a US-Malawi collaborative team that includes scientists and physicians from ICAP at Columbia University, Partners in Health, and the Ministry of Health in Malawi. They have provided us with access to a series of exceptional datasets.
Recently Completed Project
Identifying travel-time inequities in Malawi, Zambia, and Eswatini
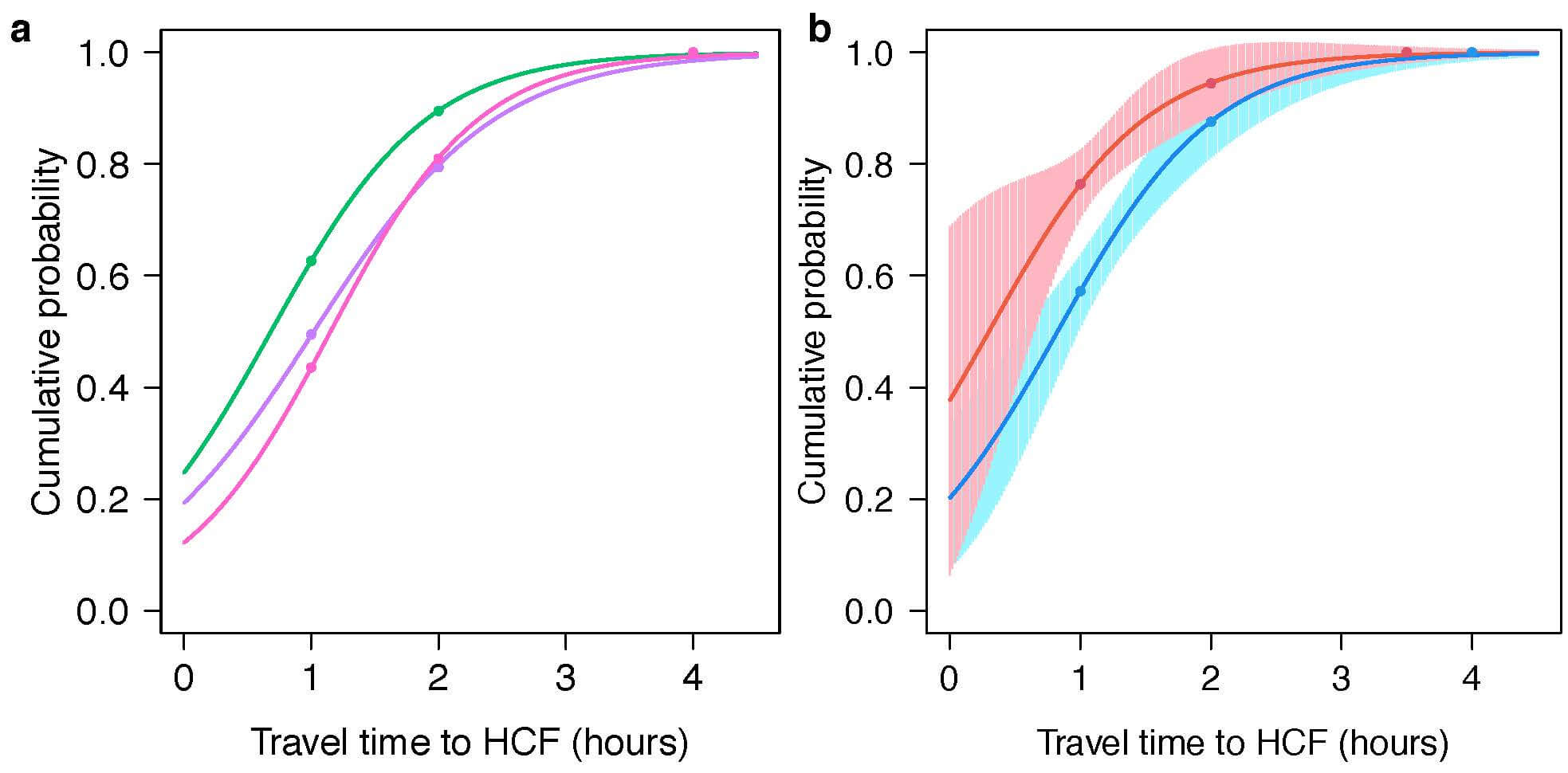
We used data from the nationally-representative Population-Based HIV Impact Assessment surveys for Eswatini, Malawi, and Zambia to identify inequities in (one-way) travel-time to access treatment. We found considerable inequities. Patients in Eswatini had the shortest travel-times; patients in Zambia had slightly shorter travel-times than patients in Malawi. Some patients traveled for less than an hour, many for more than two hours: 21% (Zambia), 19% (Malawi), and 11% (Eswatini). On average, it took longer to access ART in rural (versus urban) areas. Women in Eswatini and Zambia spent more time traveling to access treatment than men. To achieve UNAIDS’ goal of eliminating inequities in accessing antiretroviral therapy, strategies to minimize inequities in travel-time need to be designed.
The figure shows travel-time inequities. (a) National-level travel-time differences between Eswatini (green), Malawi (pink) and Zambia (purple). (b) Urban (red)/rural (blue) travel-time differences for Eswatini. Dots show the cumulative proportion of individuals traveling for antiretroviral treatment. Fitted curves are Logistic CDFs, shaded regions show 95% confidence bands for these curves.